1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
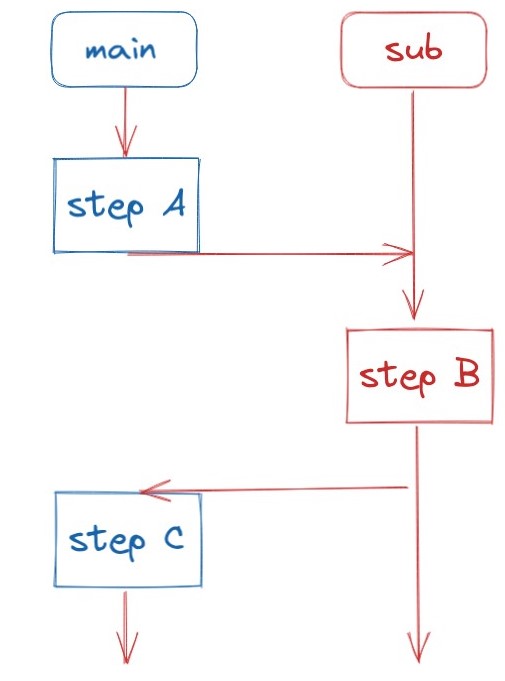
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int work_flag_g = 0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex_g;
pthread_cond_t cond_g;
static void * func(void *arg)
{
printf("Time: %d sub thread work step %d\n",
(int)time(NULL), work_flag_g);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_g);
while (work_flag_g != 1)
pthread_cond_wait(&cond_g, &mutex_g);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_g);
printf("Time: %d sub thread work step %d\n",
(int)time(NULL), work_flag_g);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_g);
work_flag_g = 2;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_g);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_g);
printf("Time: %d sub thread work step %d\n",
(int)time(NULL), work_flag_g);
sleep(1);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
printf("Time: %d sub thread work step %d\n",
(int)time(NULL), work_flag_g);
sleep(1);
pthread_t pid;
pthread_create(&pid, NULL, func, NULL);
printf("Time: %d sub thread work step %d\n",
(int)time(NULL), work_flag_g);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_g);
work_flag_g = 1;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_g);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_g);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_g);
while(work_flag_g != 2)
pthread_cond_wait(&cond_g, &mutex_g);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_g);
printf("Time: %d sub thread work step %d\n",
(int)time(NULL), work_flag_g);
sleep(1);
pthread_join(pid, NULL);
printf("Time: %d sub thread work step %d\n",
(int)time(NULL), work_flag_g);
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
|